Risk in DFS (Digital Financial Service) framework
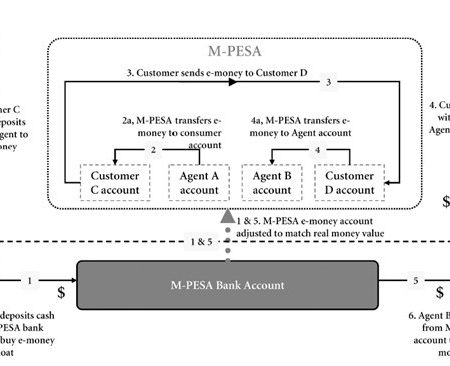
Low-income masses, micro-entrepreneurs and rural populations were previously left out of the financial market due to the high costs of physical expansion are now accessing financial services (payment, deposit mobilization) through mobile phones and networks of agents acting as representatives of financial service providers. This has resulted in a remarkably rapid increase in financial inclusion in countries. It is expected that the expansion of digital financial services will make an important contribution towards the goal of reaching universal financial access by 2020. However, with the many opportunities provided by groundbreaking technology and innovative business operations also come risks.
| Stakeholder | Key Challenges | Risk type | Implementation Difficulty
(Cost/Time) |
Intervention
Type |
|||
| Operational | Strategic | Lower | Higher | Operational | Institutional | ||
|
Customer |
Customer’s identity is stolen and used to open a MFS account fraudulently |
✔ |
✔ |
✔ |
|||
| Customer’s account security credentials, account information and transaction history are compromised | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Customer is charged unauthorized fees by agents | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Customer cannot cash-out from MFS account due to lack of agent’s liquidity | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Customer takes-out cash that proves out to be counterfeit | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
|
Agents/ Distributors |
Agent/distributor is suffering from liquidity crisis. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| Agent/ distributor is robbed. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Agent takes-in cash that proves out to be counterfeit. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Agent/distributor is unable to easily liquidate e-money inventory when the agency relationship is terminated. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Distributer’s and agents business opportunity is restricted by exclusive contract with an MFS provider. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
|
MFS provider |
Prevalence of OTC transaction | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | |||
| MFS provider fails to properly select, train and supervise agents and distributors. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Trust fund is inadequately funded. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Lack of interoperability opportunities | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Limited usage of local language for executing MFS transaction | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| Customer loses e-float balance due to the failure of bank-holding trust fund. | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
| System availability not duly ensured
|
✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ||||
* Strategic risk is broadly defined as the actual losses that result from the pursuit of an unsuccessful business plan or the potential losses resulting from missed opportunities. Strategic risk is a broader-category of risk to which MFS value-chain is exposed. Strategic risk encompasses regulatory risk, reputational risk, asset management risk and partnership risk.
* Operational risk is inherent in any business and refers to risks associated with products, business practices, damage to physical assets, as well as the execution, delivery and process management of the service. Operational risk is a broader-category of risk to which MFS value-chain is exposed. Operational risk will encompass technology risk, fraud risk.
Blog Writer: Hussain Ahmed Enamul Huda








Leave a Reply